전제 조건
- Microservices
- Api Gateway - http://localhost:9100
- WebServer(Nginx) - http://localhost:4300
- frontend - Angular
- backend - Spring boot
여러가지 문제에 대해 고민함.
- WebServer와 APIGateway를 함께 쓰는게 맞는 것일까?
- 따로 쓴다면 WebServer없이 APIGateway만 쓰는게 맞을까?
- 함께쓴다면 WebServer 가 앞일까 APIGateway가 앞일까?
- 정적파일은 WebServer에 있는게 맞다고 볼 때 APIGateway만 사용한다면 결국 WAS가 (APIGateway라곤 하지만) 정적파일을 관리하는 것 처럼 보이는데 아닌것 같은데?
- WebServer와 APIGateway를 같이 쓸 때 정적파일에 대한 Routing은 WebServer가 모두 관리할 때.. 인증 또는 권한에 따라 접근 가능한 Page는 어떻게 처리할 것인가?
- 5.에 대한 해답으로 Angular Guard를 사용하면 될 것 같은데 모두 커버가 가능할까?
- WebServer와 APIGateway를 분리함으로서의 이점들은?
우선 모든 문제에 대한 답을 찾기 이전에..
고민 끝에 WebServer와 APIGateway를 함께 쓰기로 결정함.
- WebServer가 정적파일들을 관리하는게 맞다고 주관적으로 판단함.
- APIGateway는 이름대로 API 요청에 대한 Gateway 역할(주 역할)만 해야 된다 주관적으로 판단함.
나름 아래와 같게 Architecture 를 설계해서 개발함.
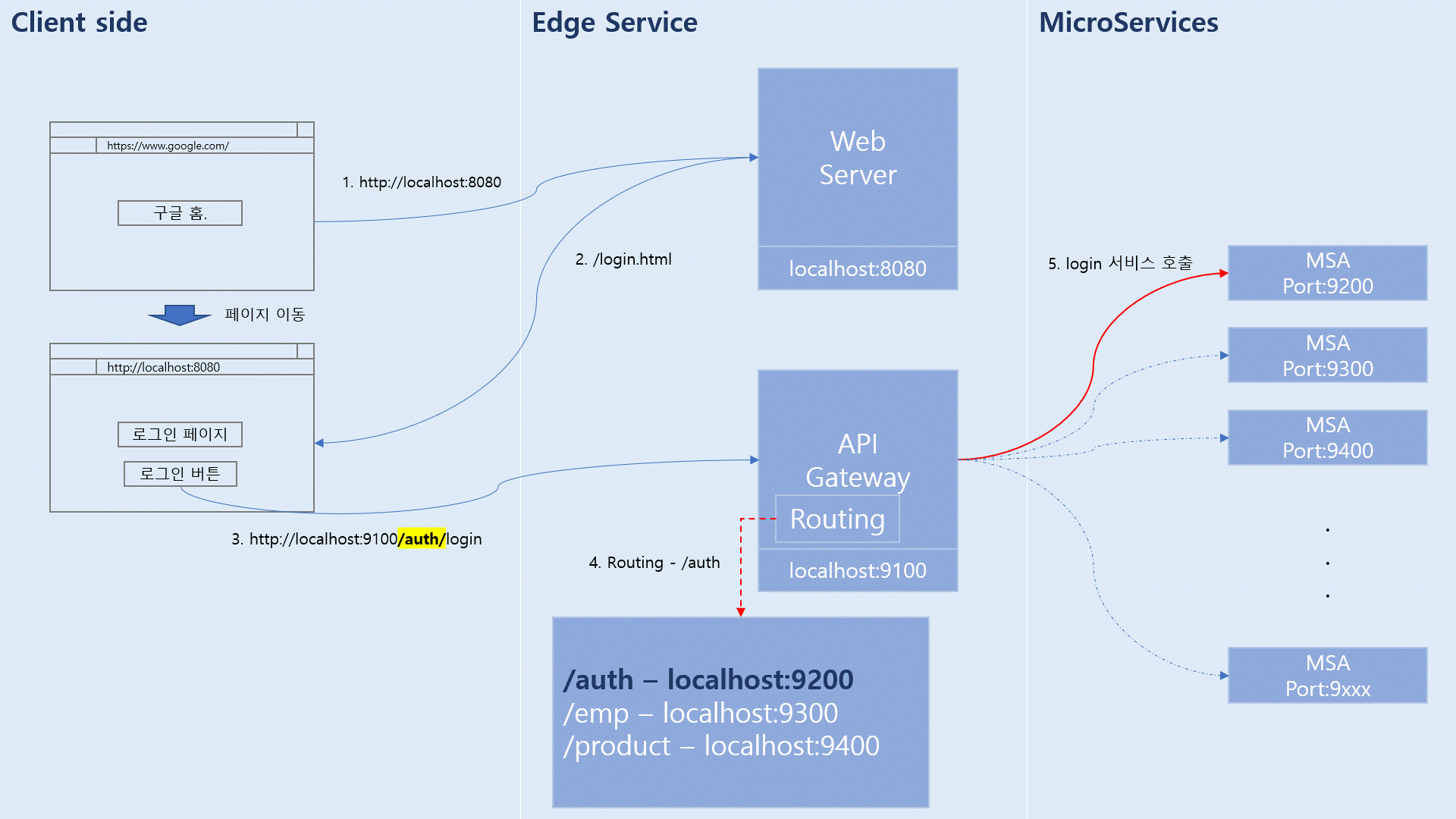
Angular 에서 정적파일에 대한 요청은 Router를 사용
Router - @angular/router
router.navigate([‘/login’])
Http요청은 HttpClient를 사용
HttpClient - @angular/common/http
HttpClient.get<Emp>(url, body)
HttpClient.post<Emp>(url, body)
정적파일에 대한 요청은 현재 브라우저가 가리키는 동일한 출처인 웹서버에 요청을 보내는 것이기 때문에
아무런 문제가 발생하지 않는다.
localhost:8080 에서 loclahost:8080 으로 요청
하지만!!
api 요청의 경우는
localhost:8080 에서 localhost:9100 으로 요청으로
동일한 출처가 아니기 때문에 오류 발생! (Cors)
이 문제를 해결하기 위해서는
APIGateway 에 Cors 설정을 해준다.
우선 동작이 가능하도록만 설정.
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.CorsRegistry;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.WebMvcConfigurer;
@Configuration
public class CorsConfiguration {
@Bean
public WebMvcConfigurer corsConfigurerDefault() {
return new WebMvcConfigurer() {
@Override
public void addCorsMappings(CorsRegistry registry) {
registry.addMapping("/**")
.allowedOrigins("*")
.allowedMethods("GET", "POST");
}
};
}
}
정책이 없는 너무 개방되어 있는 cors 설정 수정 필요
여기서 또 다른 문제가 있다.
Angular에서 모든 요청에 대해 url 을 명시해야 한다.
httpClient.post<>("/auth/login") 이렇게 적던 것을 다른 서버에 요청을 보내기 위해
httpClient.post<>("http://localhost:9100/auth/login") 이런식으로 명시해야 한다.
이부분을 해결하기 위해 Interceptor를 적용함. (bestpractice는 무엇일까..)
import {HttpEvent, HttpHandler, HttpInterceptor, HttpRequest} from '@angular/common/http';
import {Observable} from 'rxjs';
import {Injectable} from '@angular/core';
@Injectable()
export class UrlPathChangeInterceptor implements HttpInterceptor {
intercept(req: HttpRequest<any>, next: HttpHandler): Observable<HttpEvent<any>> {
req.clone({ url: `http://localhost:9100/${req.url}` });
return next.handle(req);
}
}
코드에 명확한 url 주소가 있는것 수정 필요..
Routing 처리에 대한 설명과 세부적인 구성은 제외했음…
여기까지 하게 되면 위에서 설계한 Architecture 와 동일하게 동작한다.
아직도 해결해야 할 부분이 많이 남아 있다.
시간이 되면 정리하는 걸로..